Both UDIMM and DIMM are types of rams. To compare a UDIMM and a DIMM, you would first need to know what each term means. In this article, we would take an individual look at each of the terms and see which is better in a head-to-head contest. Let’s Know more about Udimm VS Dimm
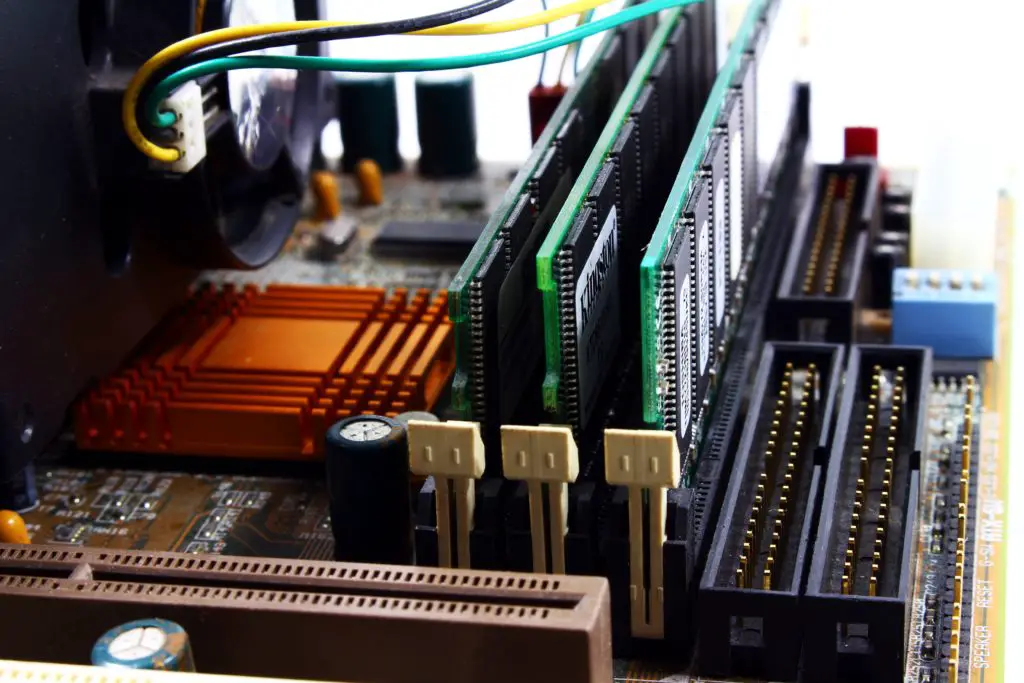
UDIMM
A UDIMM (Unbuffered dual inline memory module) is a type of memory that uses a microprocessor to transfer data from several memory modules. It is mostly used in systems with a memory channel of one or two modules. A computer system can have numerous integrated memories than cannot harm the memory. Unlike notebooks and some other computers with exactly four memory slots, other computers that are considered to have buffered memories have more than four slots.
Understanding UDIMMs
While DIMMs are mostly required for servers and workstations, UDIMMs are not. You should know that UDIMMs do not have the microprocessors that are available in a buffered memory module. You should also note that numerous full-sized DIMMs are also UDIMMs.
DIMMs
A DIMM can be considered as a computer memory that contains RAM (Random access memory) and also encourages swift data transfers. A DIMM contains DRAM circuits (Dynamic random access), and it is the most widely used memory in several high-performance computers today. With a standard height of 1.18 inches and a width of 5.5 inches, DIMMs are 64 bits of data memories.
Understanding DIMMs
DIMMs are simply double-sided single-in-line memory modules that transfer data at faster rates, with twice the data path. You should also note that DIMMs are classified into RDIMMs and UDIMMS, hence the reason why most DIMMS can also be RDIMMs.
Differences in terms of uses
DIMMs offer better stability due to their low electrical loads in terms of memory control. They are more scalable and reliable than UDIMMs, thus making them give an optimum performance which makes this memory type more efficient in servers where high-performing and high-capacity RAMs are necessary.
UDIMMs on the other hand are cheaper and less efficient than RDIMMs. They are used in the everyday laptop and desktop which requires a much lower memory. With a memory range of 2GB to 8GB, they offer average performances.
Differences in terms of features
While the DIMM is registered, the command line, clocks, and addresses are buffered while data flows freely in and out of the DRAMs and memory controllers. This memory controller pushes instructions to the clocks, addresses, and commands to the register of the memory, instead of direct access to the DRAM. Doing this reduces the electrical load of the memory controller, and significantly improves the signal integrity, thereby maintaining stability while allowing support for more memory modules from the system. It further makes it more reliable but includes a parity detection feature. The memory controller gets an error signal back to the RDIMM, which is detected by the control and address signal that passes through the register.
However, for UDIMMs, the memory controller can only detect control and address signal errors at a later stage. This is due to the lack of a parity check feature, with an exception for UDIMMs with ECC. UDIMMs can only handle a small number of DIMMS, as a high number of electrical load is being added to the memory controller with the absence of a buffer to detect any control and address signal.
Differences in terms of bandwidth and latency
Because of the additional step of traversing an address and command line to the registry, the RDIMM provides additional power and clock circle, which results in lower bandwidth and higher latency. With an 8.7% faster and more efficient data rate for two DIMMs per memory channel, the RDIMM has an even more superior performance.
UDIMMs are limited to a total number of two DIMs per memory channel at maximum with a single clock cycle working two functions to give room to settling time, which in turn results in a lesser bandwidth and a high latency.
DIMM of the future
With four different generations of DIMMs (DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4), the 5th generation of DIMM has now been unveiled. With only one compatibility with a 12th-generation desktop processor (Alder Lake), the DDR5 is meant to be an upgrade of the DDR4 as AMD prepares to produce its compatible memory chip in the year 2022. Despite having a performance rate of 4,800 MHZ-5,600 MHZ, the DDR5 consumes even less power than the DDR4. Unlike the DDR4 which has a capacity of 32GB per memory stick, the DDR5 offers a capacity of 128GB per memory stick.
In the case of a DIMM Malfunction:
- Put your server power mode on standby.
- Check to see if the DIMM is compliant with the DIMM population rule.
- Press the DIMM to remind button to check the DIMM fault led.
- Unplug the server from its power source and remove the DIMM from the memory slot.
- Check for any dust or contamination from the DIMMs connectors, and also check for any crack or damage in the DIMMs slot.
- In the case of a damaged DIMM slot, replace it and if it is dusty, gently clean it properly.
- Plug the server back to a power source and turn it on to rerun a test.
- Check your log files again.
Conclusion
It is important to know that numerous UDIMMs can also function as DIMMS and a UDIMM is a type of DIMM as well.
FAQ
- When can my UDIMM be changed?
A UDIMM should only be changed when you need to upgrade or replace a bad UDIMM memory chip.
- Can a DDR3 work in a DDR4 DIMM memory slot?
A DDR3 DIMM cannot function or fit into a DDR4 DIMM memory slot.

