
Lewis Structure of Sulphur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide is a chemical compound that has SO2 as its chemical formula. It’s a toxic chemical that has the scent of a burning matchstick. SO2 is commonly generated by volcanic activity and is created by burning fossil fuels tainted with sulfur compounds. It is a gas that is thick, colorless, and poisonous. It occurs naturally in volcanic gases and solutions in the waters of certain hot springs. Simultaneously, SO2 is typically prepared industrially by burning in the air or using sulfur compounds such as iron pyrite. In this article, we’ll know about the Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry for Sulfur Dioxide.
And in the combustion of fuels having Sulphur, large amounts of SO2 are produced. It will merge with water vapor in the atmosphere to form H2SO4, an important part of acid rain. Gas can be prepared in the laboratory by reducing H2SO4 to H2SO3, broken down into H2O and SO2, or treating sulfuric acid salts with potent acids, such as HCL. At room temperatures, sulfur dioxide can be liquefied under mild pressures. While its key uses are preparing H2SO4 (sulphuric acid) and SO3 (sulfur trioxide), SO2 is even used for cleaning, preserving dry fruits, and so on.
To draw the Lewis structure of Sulphur dioxide, you need to follow the below steps:
- First of all, arrange eight valence electrons on sulfur.
- As you might know that six valence electrons are each of oxygen and sulphur. And you have two oxygen atoms with you, so the total number of valence electrons changes from six to eighteen.
.. .. ..
: O: S: O:
.. ..
- Position the Sulphur atoms at the core and the atom of Oxygens beside Sulphur.
- The pair of electrons between the atoms are then placed in to create bonds.
.. .. ..
O:: S:: O
.. ..
- Now, start estimating formal charges to achieve the best SO2 Lewis dot structure.
- To estimate the formal charges of oxygen (O2) and sulphur (S), you need to use one formula, i.e., Number of valence electrons – No. of Bonds – 2X (No. of lone pairs)
- After using the above formula, you will get the formal charges of oxygen and sulphur that is 0
- Now, by completing the octet using O, which is a very electronegative feature, you can shape the structure of SO2.
- Then, with each oxygen atom (O2), attach a double bond and an individual lone pair.
- Finish the arrangement by positioning on the central atom the remaining electrons. Since you have four pairs of bonds and loans, the total electrons used would be 16.
- So, the number of electrons left would be 18-16 = 2. Place these electrons on the Sulphur atom, and the final SO2 Lewis structure is going to be like:
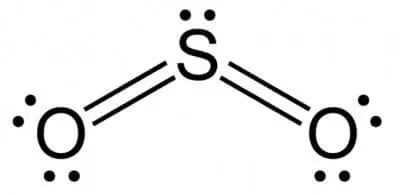
Properties of SO2
- It is a colorless gas with the taste of a rotting egg.
- In water, it is strongly soluble.
- Liquefies easily.
- Sulfur dioxide is acidic in nature as it dissolves to form sulfurous acid in water.
- Neither supportive of combustion nor combustible.
- Sulfur dioxide is an effective oxidizing agent.
- It also serves as an agent of reduction.
How is Sulfur Dioxide made?
- SO2 is prepared using many processes, the most common of sulfur or pyrite combustion (FeS2). For the implementation of this reaction, several furnaces have been produced. Each kind of furnace emits the sulfur dioxide of various purities.
- The SO2 is typically cooled and compressed during processing to transform it to liquid form because it can be processed and shipped efficiently compared to the gaseous form. As a by-product of various manufacturing processes, in particular the smelting of metallic ores, sulfur dioxide is also acquired. Smelting is the mechanism by which, by air heating, a metal is separated from its ore. This method also results in sulfur dioxide formation since many ores are sulfides, which can be collected as a byproduct of the activity.
Finally, the direct combustion of sulfur itself will create sulfur dioxide as well:
S + O2 x SO2
Molecular Geometry of SO2
Sulphur dioxide’s molecular geometry is the same as that of carbon dioxide. Consequently, SO2 bonding is as follows:
O === S === O
You can now consider the locations and number of electrons spread between Sulphur (S) and Oxygen (O2) to verify the exact form of Sulphur dioxide. Sulfur has six electrons, while oxygen (O2) has four electrons at the external level, among which one electron is used for every bond. So, in five pairs, there are 10 electrons, among which two different double bonds use two pairs together and are shaped as a single entity. Since four pairs are a must to establish bonds, one of the two double bonds makes two pairs and forms a single unit. Therefore, you might assume that V-Shaped or Bent is the molecular structure of SO2.
Uses of SO2
- At Home
- It is a substance that is very volatile in nature and should be treated carefully. Because of the dangers involved with it, it has very few applications at home. It is used in drain cleaners or as disinfectants, which encourages home cleaning.
- Drug Production
- It is used in the manufacturing of chemotherapy medicines to harm cancerous cells. It is also used in ointments to cure different skin diseases and is a fundamental component in the Debacterol ointment used in treating cancer sores.
- Industrial Use
- SO2 is used in various industries, such as the manufacturing of wastewater, the manufacture of washing agents, the manufacture of explosives, and the manufacturing of aluminum sulfate [Al2(SO4)3] in the paper industry.
Sum up
In order to sum up a few points in this article, we can say:
- Formal charges are significant to get a good Lewis structure of Sulphur dioxide.
- SO2 has various uses in different fields such as at home, for making medicines, etc.
- It has a V-Shaped or bent molecular structure.
- It is strongly soluble in water.

